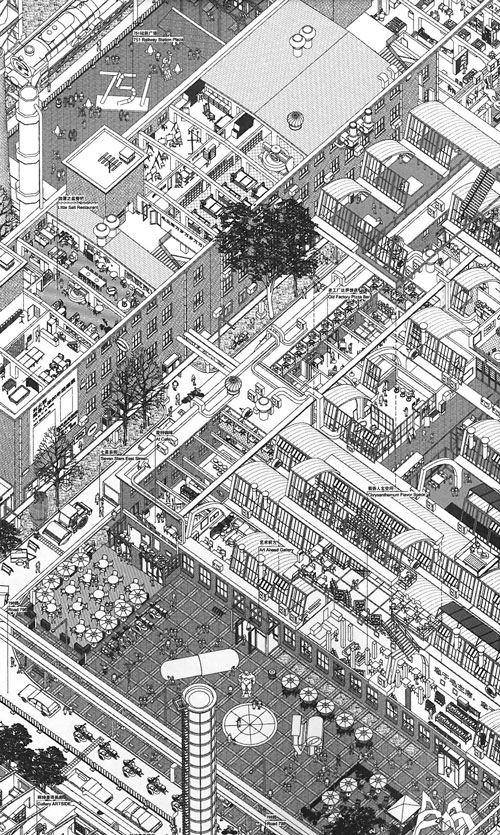
When China opened up and became a socialist market economy, it didn’t take long for the real estate sector to emerge and start developing the contemporary Chinese city according to the logic of capital, demand and supply. Even while many companies are still state-owned. For years, the traditional alleyway neighborhoods of central Beijing, called Hutongs, were a playing ground for profitable big scale redevelopment projects, tabula-rasa style. At some point, however, residents and critics became aware of the economic and cultural value of the small-scale homes in the Hutong, leading to long and difficult recompensation processes.

During Beijing Design Week 2013 I visited the Dashilar Hutong, and later that week a few other expamples. Professor Wu Chen, also director of the Beijing Institute for Architectural Design (BIAD), presented the transformation process of Dashilar, a very central and traditional hutong, close to Tian´anmen square. Earlier that day, Jia Rong of the Dashilar Project had given us a tour. The neighborhood is to a large extent made up of one and two-storey buildings from the Ming en Qing dynasty era, with the typical structure of courtyards. The complex property situation (leases, land use rights etc.), restrictions to building heights and costly expropriation arrangements have turned Dashilar into an area that is hard to redevelop at a profit by the (state) development companies. At the same time, developments are required, since the infrastructure, sanitation and public space in the area are precarious.


Dashilar Hutong (left) and Nanluoguxiang Hutong (right), Beijing
Therefore BIAD has been working for years already on an alternative development strategy. Among other measures to make people concious about the cultural value of the area, the Dashilar Phone-App was developed, through which tourists and visitors can easily explore the labyrinthic hutong and constantly receive information about design galleries, restaurants and other features in the streets of Dashilar. In collaboration with local investors, a shopping center with housing on top is being realized, avoiding the standard ‘closed box’ typology. At the same time, the infrastructure is enhanced. A new public toilet is under construction, since many of the small dwellings don’t have their own toilet. Professor Wu summarizes the project as ´Nodal development´ as opposed to the modernistic ´Tabula Rasa´ development.

Vertical hutong project, by Steven Holl, Beijing
The permeable hutong-model with its narrow alleys was abandoned by the upcoming middle class in the 1980’s and 1990’s. The old and precarious structures – many times without a proper bathroom or connection to water and the sewage system – were easily changed for modern appartments in superblock tower buildings beyond the 3rd ringroads of Beijing. The hutong, however, is making a comeback. The new generation likes going to famous hutongs for leisure. The centrality and function mix of many hutongs have become much appreciated, since Beijing now suffers from massive traffic infarcts and monofunctional suburbanization. Architects like Steven Holl and Riken Yamamoto have realized housing complexes in Beijing, conceived as modern, vertical, hutongs. In their project Meta:Hutongs, architects Wang Shuo and Andrew Bryant organize workshops to explore the possiblities of the hutong model, without taking sides of either the preservationists or the demolitionists. It is one of the projects featured in the Abitare China #34, a special magazine on Hutong Adaptation.
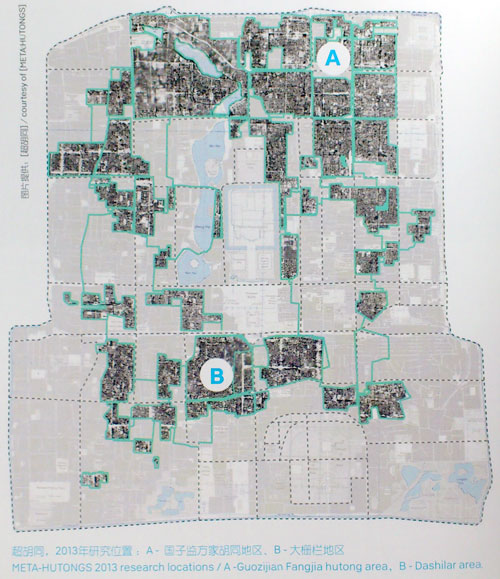
The hutongs in the central area of Beijng (within the 3rd ringroad) can easily be explored in three dimensions using Baidu Maps: